Why E&E is the Top High-Technology Export of Malaysia?
Malaysia’s electrical and electronics (E&E) sector, with its origin in the 1970s, has evolved admirably over the decades. Led initially by eight pioneering companies, known as the “8 Samurais”. Including Intel, Texas Instruments, and Hewlett-Packard (now Agilent). This industry has come a long way through continuous advancements and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies. These measures helped E&E mature into a dynamic and thriving industry.
Today, Malaysia is recognized as a major player in the growing global E&E landscape. It has big export destinations like Singapore, Hong Kong, the United States, the People’s Republic of China, Japan, and Europe. The E&E industry benefits from a collaborative environment where regional champions work together with international corporations from different countries. For example, the USA, Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, and Europe. Together, they manufacture a variety of products, from semiconductor components to consumer and industrial electronics.
| Sectors |
Sub-Sectors |
Products |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Components | Semiconductors, passive components, printed circuit boards, metal stamped parts and precision plastic parts. |
| Consumer | Audio visual products such as television receivers, portable multimedia players (PMP), speakers, cameras and electronic games. | |
| Industrial | Multimedia and information technology, products such as computers and computer peripherals, telecommunications equipment and office equipment. | |
| Electrical | Electrical | Boards, panels and consoles, switching apparatus, lamps, air conditioners, vacuum cleaners, ovens, transformers, cables and wires, primary cells and batteries, solar cells and modules. |
What role did the "8 Samurai" play in Malaysia's E&E success?
The country’s E&E sector has gone through admirable growth. Here are some key milestones and developments such as: the 8 Samuais era, expansion and diversification, global integration, industrial master plans, economic contributions, and future outlook.
Development and Milestones
The “8 Samurais” era (1972- late 1980s) describes the period when the E&E industry began with eight companies. These companies are Intel Malaysia, Hewlett-Packard (now Agilent), National Semiconductor (now Texas Instruments), Clarion, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), Bosch, Litronix (now Osram), and Hitachi (now Renesas). They worked building a strong basis for Malaysia’s E&E future. They were the first to introduce cutting-edge technologies and practices and to bring significant foreign direct investment (FDI) to Malaysia. Also, they worked to upskill the local workforce, particularly in engineering and manufacturing.
Expansion and Diversification, over the decades, this industry transitioned from basic component manufacturing to include advanced semiconductor devices, consumer electronics, and lastly industrial electronics. It contributed to 13% of back-end operations like chip packaging and testing. Regional firms have integrated into the global value chain, providing products and services to international companies. Malaysia also followed innovations like Industrial Revolution 4.0 and AI to increase competitiveness.
Malaysia has become an important player in the semiconductor market worldwide. It is attracting multinational corporations from different countries. For instance, the USA, Japan, South Korea, and Europe. The E&E sector accounts for almost 40% of Malaysia’s total exports.
Industrial Plans and Initiatives
Industrial Master Plans, the nation’s government helped this field by introducing strategic plans like the Industrial Master Plan 3 (IMP3) and the New Industrial Master Plan 2030 (NIMP 2030). They focus on innovation, R&D, and high-value manufacturing. Besides these plan, Malaysia’s government launched several other initiatives like:
- The Twelfth Malaysian Plan
- National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR)
- National Artificial Intelligence (AI) Development Plan
- Malaysia External Trade Development Corporation (MATRADE)
Economic Contributions, the E&E industry has continuously been a major contributor to Malaysia’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment, and exports. For example, in 2023, Malaysia exported products worth $312,7 billion, more than the year prior. By 2025, the sector is expected to generate RM495 billion or $113 billion in export revenue. These amounts underscore the E&E industry’s paramount role in Malaysia’s economic improvement.
Factors Behind E&E Success
Malaysia’s Electrical and Electronic (E&E) industry has a challenging path and has reached remarkable levels. Its success is thanks to several key factors:
Government Policies
Malaysia’s government has a crucial influence in nurturing the E&E sector through different measures:
- Tax incentives: This country provides beneficial incentives to local and foreign investors. For example, the groundbreaker status, reinvestment allowance, and investment tax allowance.
- Industrialization strategies: Malaysia’s government introduced strategic plans that focus on a range of points. Such as, enhancing economic complexity, promoting high-value manufacturing, and developing clusters for innovation and R&D.
- Infrastructure development: This country has invested heavily in infrastructure to support industrial growth. It chose this path to fund in: modern ports and highways for efficient logistics, advanced telecommunications networks, and eco-industrial parks to promote sustainability.
Geographical advantage
Malaysia’s strategic location offers crucial advantages in the global supply chain. It is situated at the crossroads of major maritime trade routes, between the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea. Making it a perfect center for shipping and logistics, uniting the East and the West.
Also, Malaysia’s location provides access to ASEAN markets and more. It is near major economies like China, India, and Singapore, underlining its role as a regional logistics and manufacturing hub. The country’s contribution to free trade agreements and regional economic initiatives further strengthens its position in global supply chains. These agreements provide businesses with access to a vast consumer base.
Skilled Workforce
The country’s talented labor force is the foundation of its thriving Electrical and Electronics industry. And here is why:
- Education and training in Malaysia are provided by over 1,400 vocational education and training (TVET) colleges. Along with public and private universities, which aim to equip students with industry-related abilities.
- Multilingual proficiency, the Malaysian labor force is often multilingual, with good English proficiency. These qualities are crucial for employment and global collaboration.
- Industry collaboration and partnerships between industries and educational facilities increase workforce preparation. These collaborations include internships, hands-on training, and specialized employer training programs.
Technology Adoption
Malaysia’s E&E industry has adopted technology as a driver of its success. Taking the needed measures, initiatives, and solutions. Following Industry 4.0 practices is fundamental for E&E’s success. Automation, smart manufacturing, and up-to-date technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics increase efficiency and production abilities. The embracing of innovative methods reduces operational costs, improves quality, and opens doors to new creations like 5G-enabled devices or energy-efficient systems. This integration of modern automation and smart manufacturing has positioned the country as a significant player in the semiconductor supply chain.
Research and Development (R&D)
This nation is focusing on Research and Development (R&D) to nurture innovation in the E&E field. Funds from international corporations and government reforms led to improvements in areas like integrated circuit (IC) design, semiconductor testing, and energy-efficient technologies. These areas follow the leading trends and ensure the country’s relevance in the international market. There are also collaborations between the private and the public domains. Partnerships between education, private firms, and government facilities are crucial for improving R&D. These collaborations focus on experimental development and the commercialization of innovative technologies.
These practices highlight Malaysia’s dedication to nurturing a vibrant R&D environment in the E&E sector.
Major Companies in Malaysia's E&E Sector
The E&E industry boasts many prominent companies that have significantly contributed to its growth and global reputation. Here are some major players:
Globetronics Technology Berhad
This company specializes in semiconductor manufacturing and has been an important contributor to Malaysia’s E&E exports. Their innovative solutions in sensor technology and LED manufacturing have positioned them as a leader in the industry.
Inari Amertron Berhad
Inari Amertron is another important player, focusing on outsourced semiconductor assembly and testing (OSAT). Their collaborations with multinational tech giants have helped Malaysia maintain its competitive edge in the semiconductor market.
The firm stands out in renewable energy and energy efficiency solutions, including PV solar systems and sustainability infrastructures. Their focus on green technology aligns with Malaysia’s desire for sustainable development.
ODIN Engineering
ODIN Engineering is known for its innovative engineering solutions and operates across different regions in Malaysia. Their professionalism in technology-powered projects has made them a valuable asset to the E&E sector.
These companies, among others, are driving Malaysia’s E&E industry forward through innovation, collaboration, and a dedication to excellence.

Contributions from Multinational Corporations
Multinational corporations (MNCs) have played a transitional role in Malaysia’s E&E sector, contributing to its global prominence.
- Semiconductor giants, manufacturing, and R&D facilities in Malaysia were established by several companies. For instance, tech companies like Intel, Texas Instruments, and AMD. They introduced modern technologies and practices, upgrading Malaysia’s abilities in semiconductor production.
- Economic impact, multinationals took part in improving Malaysia’s GDP through significant foreign direct investments (FDI). These funds are projected to generate over 26,668 new work positions, including roles like engineers and technicians.
- Skill development, where these corporations provide training and upskilling opportunities for the regional labor force. Initiatives like the Industrial Upskilling and Reskilling Programme aim to equip the workforce with advanced skills in different domains. These include fields like integrated circuit (IC) design, engineering, and testing. To make sure that Malaysia remains competitive in the global market.
- Global supply chain integration, Multinational corporations have positioned Malaysia into the global E&E supply chain. It makes this nation an important player in the production and export of semiconductor devices and other electronics.
Malaysia’s Electrical and Electronics (E&E) domain is a foundation of its industrial growth. It is driven by both local champions and multinational corporations (MNCs).
Global Competitiveness
The country E&E is an important factor that contributed to the rise of the economy and remarkable global competitiveness. Due to significant exports and high demand, Malaysia is a crucial rival in the global landscape of the Electrical and Electronics industry.
Global Ranking and Comparison
The semiconductor field is one of the most prominent sectors in the global E&E industry. It ranks Malaysia among the top global exports and in the global value chain. The county’s government also invests actively in this domain, increasing its impact on the economy.
In 2023, Malaysia ranked as the sixth-largest global exporter of semiconductors. It holds about 7% of the global market share. This nation had exports valued at RM575 billion or $131.6 billion, despite a small dip in global semiconductor sales. This achievement underlines Malaysia’s rising influence in high-value-added segments of the E&E industry.
| Rank | Country | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Taiwan | ~20% |
| 2 | South Korea | ~18% |
| 3 | China | ~15% |
| 4 | United States | ~12% |
| 5 | Japan | ~8% |
| 6 | Malaysia | ~7% |
This nation, over the years, transitioned from labor-intensive, low-skilled production to higher-value-added activities. This transformation is powered by proactive investment promotion, labor force development, and government incentives. Malaysia’s strategic focus has incorporated it deeply into the global E&E value chain. Focusing on the Assembly, Test, and Packaging (ATP) segment. These measures are cementing the country’s position as a crucial player in the global semiconductor ecosystem.
In addition, Malaysia’s government has been important in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) to sustain the E&E sector. Initiatives like the Penang Skills Development Centre have increased workforce capabilities. It makes this nation attractive for multinational corporations seeking a competitive edge in the E&E market.
The High Demand for Malaysian E&E Products Internationally
The Malaysian E&E sector continues to thrive thanks to its strategic advantages and global demand. In 2024, E&E exports reached RM601.18 billion or $137.7 billion, which is a record and almost half of Malaysia’s total exports. This growth was powered by strong demand from major markets like the United States, ASEAN countries, and the European Union.
Malaysia’s beneficial location in Asia, joined with its strong framework and free trade agreements. It provides Malaysian E&E products with access to the global market of over 4 billion people. In addition, the country’s role in the semiconductor supply chain and its inclusive ecosystem for both front-end and back-end manufacturing make it a favored location for multinationals.
The nation's E&E industry is a crucial pillar of the global supply chain, highlighting remarkable rivalry and robust growth. With its strategic location, comprehensive infrastructure, and trade agreements, Malaysia has positioned itself as a preferred player in international markets.
Sustainability and Challenges
The Electrical and Electronics industry is facing some challenges due to the high competition, disruptions, and changing technologies. It is implementing some effort to sustain this sector, like reducing electronic waste, environmental issues, and green manufacturing initiatives.
Challenges
- Competition, Malaysia is battling with Vietnam and China, countries with lower costs of their products. This impacts its ability to innovate and develop high-value-added industries.
- Supply chain disruptions, the COVID-19 pandemic is an example of a global crisis that has highlighted vulnerabilities in supply chains. These situations require better coordination and resilience strategies.
- Adapting to changing technologies, the E&E sector must resolve the problem of talent shortages and premature deindustrialization. These measures are needed to remain competitive in emerging sectors, such as green technologies.
Sustainability Efforts
The Malaysian Electrical and Electronics industry is actively embracing sustainability as a main priority. Green manufacturing initiatives are at the top, with companies aiming to decarbonize operations and follow the global climate goals, outlined by the Paris Agreement.
Malaysia also has a goal to decrease electronic waste, taking measures by improving material efficiency and adopting circular economy principles. This works by recycling outdated products and minimizing waste throughout the manufacturing process.
Despite these practices, E&E continues to face substantial environmental concerns, for instance, high resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Addressing these challenges needs comprehensive assessments and more robust policy infrastructures to ensure long-term support.
Technological Advancements and Trends
Advancements in AI, IoT, and semiconductor technologies are significantly influencing Malaysia's E&E. In addition, technological innovations and case studies are another big influence on E&E's prosperity.
Technological Innovations
Malaysia is leveraging AI and IoT to increase manufacturing processes, optimize supply chains, and develop smart devices. These technologies are fundamental in creating more efficient and sustainable systems. The country has remarkable semiconductor progress, being a global leader in packaging, assembly, and testing, commanding 13% of the world’s market share. Technologies like the 2nm chip are innovations that are reshaping the industry, enabling faster, more devices that are efficient in energy.
Case Study: Penang

Penang is known as a successful case due to its combination of strategic initiatives, strong framework, and continuous innovation.
The cities progress is influenced by government initiatives like the Free Industrial Zones (FIZs). It first established tax incentives and streamlined regulation to be more appealing for FDI. Penang took measures to attract MNCs led to the building of new facilities by tech giants, including Intel, HP, and AMD.
Penang developed a dynamic industrial cluster, nurturing partnerships among MNCs, regional suppliers, and service providers. Entities such as the Penang Development Corporation (PDC) play a crucial role in coordination infrastructure development and investor relations. Skilled workforce and talent development are parte of Penang’s philosophy. Universities and technical colleges in Penang have produced a large amount of skilled graduates suited to fit the E&E industry’s criteria. Institutions like the Penang Skills Development Centre (PSDC) provide specialized training rograms. It is assuring a labor force abble to work in current technologies.
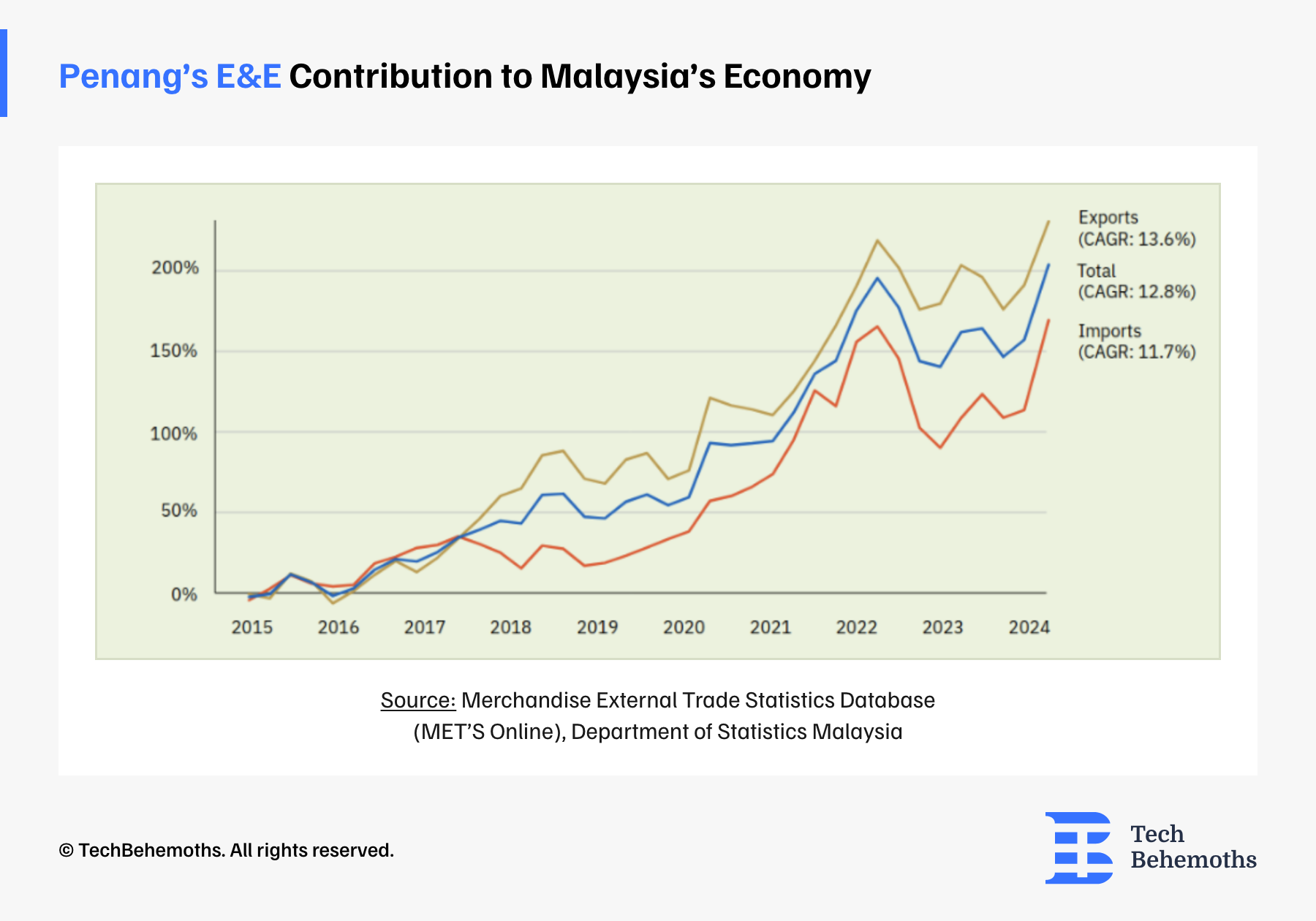
The E&E sector in Penang has evolved from basic assembly to high-value activities. Including R&D, design, and advanced manufacturing. Penang is also encouraging local companies like ViTrox that are focusing on machine vision, electronics, influencing the sector’s diversification and resilience. The Electrical and Electronics industry in Penang bringed admirable economic contributions. In 2023, Penang’s industry accounted for RM477 billion or $94.3 billion in exports, representing almost 31% of Malaysia’s exports. The manufacturing sector constitued 46.5% of Malaysia’s GDP in 2023. Penang attracted investments equal to $13.4 billion in 2023, being nearly 33% of Malaysia’s total FDI.
Penang’s progress in the E&E industry is attributed to proactive government policies, a benefic bussines environment, and the ability to adapt and innovate in response to global trends. This combinated effort has empowered its reputation as a leading center in the global electronics sector.
Future Outlook of Malaysian E&E
Under the Twelfth Malaysian Plan, the E&E industry has a goal to contribute RM120 billion or approximately $25,8 billion, according to MIDA. This amount is needed for Malaysia’s GDP by 2025, accentuating sustainable growth and tech advancements. Malaysia focuses on high-value activities, like semiconductor design and advanced manufacturing, aiming to climb further up the global value chain. Initiatives like the Semiconductor Strategic Plan (SSP), are projected to attract more foreign investments and improve local firms.
Conclusion
From the 8 Samurai to being among the global leaders in the global landscape, Malaysia’s Electrical and Electronics industry (E&E) has had a remarkable path of success. It evolved into a powerhouse through innovation, strategic policies, and partnerships. This sector could reach exports of $137.7 billion thanks to its strategic location, trade agreements, and strong manufacturing environment. These achievements are solidifying its role in the global supply chain.
Government initiatives like the Semiconductor Strategic Plan and the private R&D efforts boost tech advancements in AI, IoT, and Industry 4.0. These practices are nurturing smart manufacturing and energy-efficient innovations. Sustainability remains a priority, with green manufacturing and electronic waste reduction initiatives. These are ensuring long-term growth despite challenges like global competition and supply chain disruptions.
Malaysia’s E&E sector can climb further up the global value chain thanks to its skilled labor force, policies, and strong global collaborations. It is a foundation of economic development and a leader in advancing up-to-date technologies.
To discover more about Malaysia’s IT companies, you can look at the TechBehemoths page, finding new firms located and originated in Malaysia.