Industry 4.0 - Malaysia's Ambitions Plan to Embrace Technology

Industry 4.0 represents a transformative shift in the global economy of Malaysia. This transition is powered by modern technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and robotics. The use of these innovations is increasing efficiency, productivity, and connectivity. Recognizing its potential, Malaysia has integrated these technologies into its economy for further progress.
The government is prioritizing manufacturing to help develop infrastructures like Malaysia’s Madani Economy. It includes adding smart factory transformations, using IoT for predictive maintenance, and leveraging AI for automation. Malaysia is currently competing in the global value chain due to the adoption of Industry 4.0, which is important for the country’s manufacturing and digital sectors. This nation is aiming to participate in research and development (R&D) and design. However, there are still some challenges, including the need for talented workers and resolving the remaining infrastructure gaps.
The Fourth Industry not only boosts economic growth but also increases the quality of work and attracts skilled talent. Malaysia’s goal reflects a strategic approach to embracing Industry 4.0 and making certain sustainable development.
Background of Industry 4.0
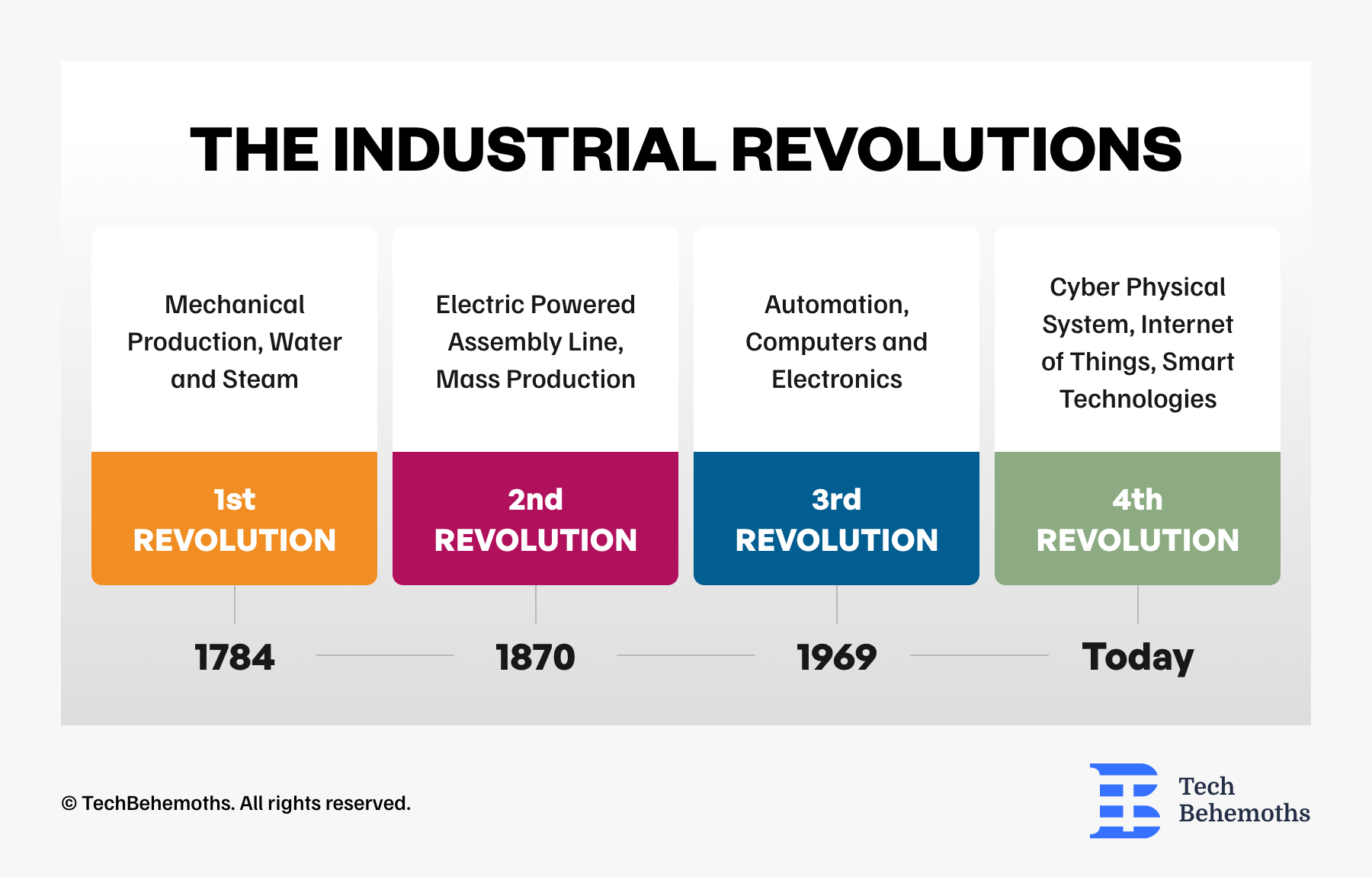
The world is currently looking for a way to permanently change how we live and work. That’s why Malaysia implemented four revolutions in the field of industry. The First Industrial Revolution was driven by steam and water power, while the Second Revolution was boosted by electric power and manufacturing procedures. The Third Industrial Revolution brought about information technology and automation. And finally the Fourth Revolution in Industry.
Industry 4.0 changes the way products are created, designed, used, and operated but also how they are serviced and maintained.
This industry actively integrates technologies and innovations to improve Malaysia’s economy and industry. Artificial Intelligence is used to provide intelligent decision-making. Meanwhile, the Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time data exchange across connected systems. Big data analytics sustains predictive insights and operational efficiency. Robotics increases exactness and productivity in manufacturing. Cloud computing facilitates a scalable digital framework.
Industry 4.0 is rapidly adopted worldwide, including in highly developed economies like Germany, the United States, and China. They are also incorporating AI, IoT, big data, robotics, and cloud computing into their industries to improve efficiency and competitiveness. These countries are prioritizing smart manufacturing, automation, and digital transformation to develop production and supply chains.
Malaysia is using Industry 4.0 to empower its manufacturing sector, attract foreign investments, and boost technological innovation. The government implemented initiatives to help Malaysia compete in global value chains. For instance, measures like smart factories, transformations, and AI-driven automation. The nation’s skilled workforce and strategic location give additional advantages in improving the smart industry.
Malaysia's Industry4WRD Initiative
Industry 4.0 has a National Policy launched on 31 October 2018 named the Industry 4WRD. Its scope is to ensure digital improvement in the manufacturing and related services fields in Malaysia. The Industry4WRD infrastructure is the following:
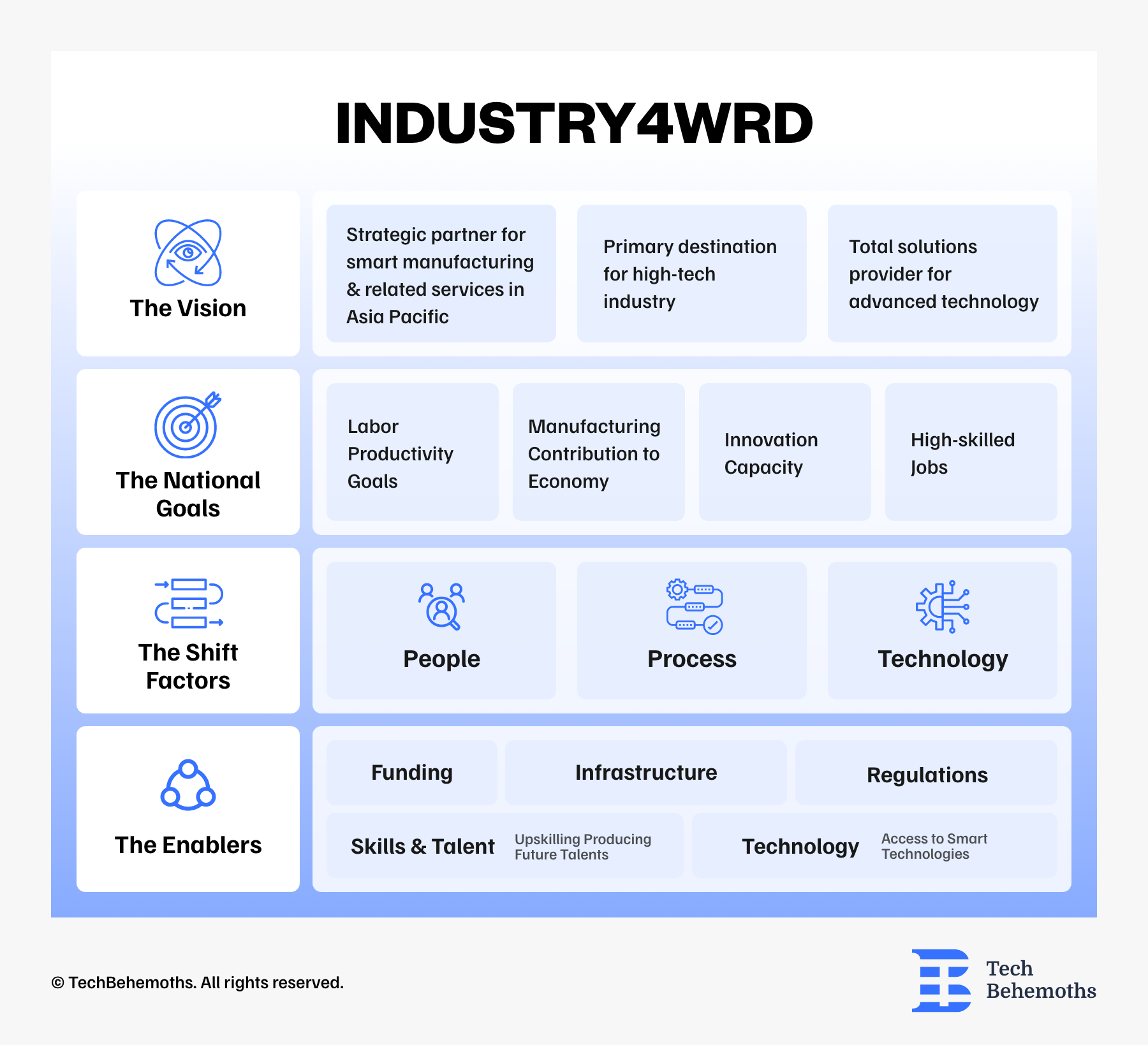
The effectuation of this National Policy focuses on creating the right framework to sustain companies in various sectors. These include manufacturing, incentives, infrastructure, human capital development, and technology facilities.
The objectives of Industry4WRD are Threefold: A-C-T.
A - Be appealing to associates with Industry 4.0 processes and technologies. Also, to raise Malaysia’s appeal as a favored manufacturing destination;
C - Make an ecosystem tailored for Industry 4.0 to be adopted and coordinate established and new development initiatives;
T - Transform the country’s industry capability in both a holistic and vigorous way.
The Industry4WRD aims to reach 3 targeted outcomes:
- Increased manufacturing sector contribution;
- More high-value-added products;
- Continuing FDIs.
Main goals
- Innovation, empowering Malaysia’s global creations ranking, and being home to a culture of technological superiority.
- Digital Transformation, promoting businesses to adopt Industry 4.0 technologies like AI, IoT, and automation.
- Competitiveness, increasing productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing domain to drive economic well-being.
- Talent Development, enhancing the number of high-skilled workers in the industry.
Industry4WRD Intervention Fund
A crucial program under this program is the Industry4WRD Intervention Fund. It provides financial support to SMEs in manufacturing and similar fields from Malaysia. The fund works on a matching basis (70:30), which means that qualified companies can gain up to RM500,000 or approximately $113,327. These funds are used to achieve digital transition projects. Its goal is to help SMEs develop their processes, technology, and people to align with Industry 4.0 criteria.
Thanks to these measures taken, Malaysia is remaining ahead in the digital revolution and continues its tech progress.

Role of SMEs in Malaysia's Industry 4.0 Goals
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) play a crucial role in Malaysia’s Industry 4.0 transition. Here is how:
Importance of SMEs in Malaysia’s Economy
SMEs are the backbone of Malaysia’s economy, having a paramount impact on GDP and employment. They are also the majority of businesses in this nation. However, their usage of Industry 4.0 technologies is in its early stages. There are four key contributions of SMEs:
- Economic Growth, powered by strong householding spending, favorable labor market conditions, and robust investments, influenced the growth of Malaysia’s GDP in 2024 to 5.1%. SME Bank projects Malaysia's GDP to rise between 4.5% and 5% in 2025.
- Employment, SMEs offer jobs to a large part of the workforce, assuring economic sustainability and possibilities for local talent.
- Innovation & Digitalization, for SMEs to remain competitive, they are incorporating advanced digital technologies like AI, IoT, and big data.
- Global Trade & Investment, SMEs based in Malaysia are benefiting from foreign direct investment (FDI), which reached $3.1 billion in the first 6 months of 2024.
While SMEs are vital for financial growth, they face challenges, for example, access to funding, digital transition, and regulatory hurdles. However, government initiatives, tax incentives, and training programs are helping them adapt and thrive in the evolving economic landscape.
How can SMEs benefit from Industry 4.0?
SMEs can gain important advantages from technologies in their operations. These advancements increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve competitiveness. In addition, there are other major benefits:
- Increased productivity;
- Cost reduction;
- Better decision-making;
- Enhanced flexibility;
- Improved supply chain.
Financial and Technical Support for SMEs
Malaysia gives various financial and tech support programs to help SMEs integrate Industry 4.0 technologies and raise the country’s rating in the global rivalry. There is some economic help for Small and Medium Enterprises:
- CIP sprint & spark grants, these grants give funding for tech-based ventures, covering expenses for product sweetening and market access.
- MSME digital grant supports SMEs in following digital solutions to raise efficiency and productivity.
- Soft loan scheme for services capacity development (SLSCD) helps businesses diversify into higher-value activities and develop service delivery.
- Bumiputera Supply Chain (BSC), offers economic aid between $113,327 and $1,133,275 to ease financial difficulties for SMEs.
SMEs are a driving force behind Malaysia’s economic growth and innovation. Their role is crucial in employment, digital transition, and global trade essential for the nation’s Industry 4.0 transformation.
Collaborative Efforts Driving Progress
Collaboration is the backbone of progress, especially in the era of Industry 4.0, where innovation thrives on shared expertise and resources. Government, private enterprises, and academic facilities play an important role in shaping the future:
- Government Contribution, policymakers create infrastructures that encourage tech advancements, fund research initiatives, and sustain workforce development programs. Also, the government invests in cybersecurity, ensuring businesses have the needed safety measures to protect their digital data. In addition, training is made to help employees adapt to new technologies, for they to remain competitive in the evolving job market.
- Private Sector Involvement, businesses boost innovation by funding emerging technologies. They are home to entrepreneurship and partnerships with research institutions. Businesses work with governments to develop smart frameworks, digital manufacturing platforms, and cybersecurity architectures. In this way, businesses help develop cutting-edge solutions.
- Academic Institutions, Universities, and research centers provide the intellectual base for Industry 4.0, equipping students with the skills needed. This is made for them to navigate easily through the evolving job market and conduct studies that push tech boundaries. Also, partnerships between universities and businesses help unite theory and practice, ensuring students gain hands-on experience. In addition to this, many universities foster startups and incubators, helping students and researchers turn ideas into market-ready solutions.
Ultimately, partnerships are essential for achieving Industry 4.0 objectives. By fostering cross-sector collaboration, stakeholders can accelerate innovation, increase productivity, and create sustainable solutions for the future.
Economic and Social Impact
Industry 4.0, often referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is changing economies and societies in profound ways. It is very useful thanks to modern technologies like AI, IoT, and automation. Here are highlighted the most important implications:
Economic Impact of Industry 4.0
The Fourth Industrial Revolution changed the financial status of Malaysia in several key ways:
- Boosting productivity, automation, and artificial intelligence-powered processes increases efficiency by reducing production costs and raising the output.
- Transforming business models, companies are choosing the path leading to digital platforms, data-driven decision-making, and smart manufacturing.
- Workforce evolution, while some traditional jobs may not be appealing to it, new roles in AI, robotics, and cybersecurity are emerging and needed in the future.
- Global trade & competitiveness, countries that invest in Industry 4.0 technologies gain a favorable position in the competition, influencing global trade.
- Sustainability & cost reduction, advanced technologies optimize resource use, reducing waste and energy efficiency.
Industry 4.0 is reshaping economies at every level. It presents immense possibilities but also challenges that require strategic planning.
| Economic Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Productivity | Automation and AI improve efficiency, reduce costs, and optimize processes. |
| Global Competitiveness | Companies adopting advanced technologies gain an edge in international markets. |
| Innovation-Driven Growth | Digital transformation fosters new business models, products, and services. |
| Job Market Evolution | Demand for high-tech skills increases, leading to workforce reskilling needs. |
| Cost Reduction | Smart manufacturing reduces material waste and operational expenses. |
| Economic Expansion | Increased efficiency drives GDP growth and new opportunities. |
Social Impact of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is reshaping society in profound ways, bringing both opportunities and challenges. It brings changes in the workforce, society, and sustainability.
Automation and AI are transforming the workforce, leading to both job shifts and the creation of new jobs that require special skills. Workers must adapt continuously by upskilling themselves and learning new material. The traditional workplaces are also transitioning, adding remote collaboration and AI-powered decision-making.
Besides employment, the Fourth Revolution is influencing the way people interact with technology and businesses. Smart cities are thriving with improved urban living, while rural areas may struggle. Economic disparities could be aggravated if access to advanced technologies remains unequal. This requires governments to focus on inclusive digital changes.
| Aspect | Impact in Malaysia |
|---|---|
| Employment | Automation is reshaping the job market, reducing demand for low-skilled labor while increasing opportunities in Al, robotics, and data analytics. |
| Education & Skills | The government and industries are investing in upskilling programs to prepare workers for digital transformation. |
| Workplace Evolution | Digital collaboration and smart manufacturing are becoming more prevalent, improving efficiency but requiring new skill sets |
| Urban & Rural Development | Smart city initiatives are enhancing urban infrastructure, but rural areas face challenges in adopting advanced technologies. |
| Consumer Behavior | Al-driven services and e-commerce are transforming how Malaysians interact with businesses and make purchasing decisions. |
|
Ethical & Privacy Concerns |
Increased reliance on digital platforms raises concerns about data security and AI ethics. |
| Sustainability | Industry 4.0 technologies are helping Malaysia optimize resource use and reduce environmental impact. |
Consumer behavior is shifting as well, with AI-driven services and personalized products changing how people shop, engage with firms, and even manage their daily lives. While it may look more convenient, there are questions about data privacy. It suggests discussions about regulation and responsible innovation.
However, smart technologies are making better resource use, and reducing waste, and environmental impact. Still, these benefits must be balanced with ethical considerations. For example, automation replacing human labor, AI bias, and discussions about fair access to tech developments.
Challenges and Solutions
Resolving challenges like resource limitations, resistance to change, and cybersecurity risks requires meticulous planning and adaptability. Most of the challenges and their solutions include:
Resource limitations
Challenge: A limited budget, workforce, or framework can be an obstacle to progress.
Solution: The nation may focus on investments, improve existing sources, and expand partnerships or automation to increase efficiency.
Resistance to change
Challenge: Employees or stakeholders may resist new technologies or processes.
Solution: Countries must foster a culture of innovation, provide training, and communicate the benefits of change efficiently.
Cybersecurity risks
Challenge: The increasing cyberattacks, data breaches, and compliance issues.
Solution: Malaysia should implement strong security infrastructures like NIST. Additionally, the use of encryption, conducting regular audits, and educating employees on cybersecurity practices may also help.
Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Digital transformation: Companies and firms are training their employees and involving them in decision-making. This resulted in them successfully navigating through the evolving tech landscape.
Risk management: Organizations that resolved cybersecurity issues successfully adopted structured frameworks and coherently adapted to upcoming threats.
Case Study
BigBank’s case is an interesting study on overcoming resistance to change in a big data analytics implementation. This company is a large commercial bank in Malaysia, looking to integrate big data analytics into its operations. This will enhance decision-making and customer service. However, the transformation faced significant problems like employee resistance. These concerns are due to job security, unfamiliar technology, and workflow disruptions.
The bank faced some challenges, for example, employees were hesitant to follow new analytic tools. There were also concerns about the system’s complexity and its influence on daily tasks. Also, the fear of job displacement resulting from automation is playing a crucial role.
Still, BigBank could overcome these problems by implementing the following solutions:
- Role of translators, the bank introduced a new role named “Translators”. They are employees who act as a bridge between the analytics IT team and the business department. They help connect the technical experts and operational staff.
- Training programs and structured training were provided by employees to acquaint them with the new network.
- Gradual implementation, BigBank synchronized in the analytics tool, allowing employees to adapt gradually.
BigBank’s journey shows the importance of adaptability and communication in digital transformation. By resolving challenges and overcoming concerns, this bank proceeds to succeed and be a prime example for the following companies.
Future Vision
Malaysia has admirable long-term goals for following Industry 4.0, with its focus on transformation across various domains. The National Fourth Industrial Revolution Policy serves as a guide to make sure Malaysia stays ahead in tech advancements. The Policy emphasizes different modern and up-to-date technologies to enhance productivity and competitiveness.
In addition, Malaysia’s New Industrial Master Plan 2030 (NIMP 2030) highlights strategies to boost economic growth through smart manufacturing, e-commerce, and biotechnology. This plan aims to bridge the digital divide between urban and rural areas, increase cybersecurity, and develop a skilled workforce proficient in AI, IoT, and data analytics.
To remain competitive in global manufacturing, Malaysia is prioritizing key factors. They are autonomous production lines, smart manufacturing practices, big data tools, process flexibility, and security. The government is also fostering training to improve the skills of its workers. This is made for businesses to leverage Industry 4.0 technologies and benefit efficiently.
Conclusion
Malaysia’s Industry 4.0 transformation is revolutionizing industries by integrating AI, IoT, automation, and big data. SMEs, as the foundation of the economy, play a crucial role in innovation, employment, and digital adaptation. It has the government's support through incentives and training programs.
Disregarding challenges like cybersecurity risks, workforce resistance, and ethical concerns, strategic initiatives are ensuring sustainable progress. These initiatives are NIMP 2030 and Industry 4WRD. Partnerships between government, businesses, and educational institutions are creating a robust digital ecosystem, fostering resilience and inclusive growth.
As Malaysia grows vigorously towards a tech-powered future, its ambitious approach is paving the way to a smarter and more competitive economy.