Data Security in the AI Era: Risks, Vulnerabilities, and Best Practices for Businesses in 2025

Summary
-
AI in 2025 is both a business tool and a cyber threat — don’t ignore the risks.
-
Watch out for: hyper-realistic phishing, deepfakes, AI-driven ransomware, and shadow AI use by employees.
-
Learn from recent cases (DeepSeek, Arup): weak configs and poor identity checks = massive losses.
-
Stay compliant: align with EU AI Act, DORA, and NIST frameworks to avoid legal and operational penalties.
-
Act now: encrypt sensitive data, enforce MFA & zero-trust, clean training datasets, and monitor AI activity 24/7.
-
Prioritizing data security protects your AI systems, safeguards compliance, and strengthens organizational trust.
In 2025, we are witnessing the predictable phenomenon with the advent of artificial intelligence - companies are facing a turning point in terms of data security. From a simple support tool, AI has become the one who makes tactical decisions, more or less important for the business. It interacts with customers, participates in negotiations, solves complex tasks, and, however inappropriate it may seem for the subject addressed, is also used in cybersecurity.
As organizations adopt artificial intelligence to optimize business processes and efficiency, they must also face the uncomfortable reality that the same technology that powers their business can be used as a weapon against it.
This article explores the key risks that businesses face in the era of artificial intelligence, the hidden vulnerabilities that they often overlook, and the best practices that can protect legal entities' data in 2025 and beyond.
From Traditional Cyber Threats to AI-Powered Attacks
Unlike cyberattacks of the past decade, which often followed predictable patterns, today's risks evolve in real time through artificial intelligence-based techniques - making them faster, smarter, and harder to detect.
The table below represents how big the leap is from traditional digital threats to those generated by AI, making it inevitable for today's companies to review and strengthen their security strategies.
|
Aspect |
Traditional Cyber Threats |
AI-Powered Attacks (2025) |
|---|---|---|
|
Phishing |
Generic messages, often with obvious errors, easy to detect |
Hyper-personalized emails & messages, flawlessly written by AI, hard to distinguish from real communications |
|
Malware |
Static code, signatures easily detected by antivirus |
Self-modifying, adaptive malware designed to evade detection |
|
Attack Speed |
Manual planning and execution required |
Automated attacks launched at global scale within seconds |
|
Social Engineering |
Simple impersonations (e.g., fake bank emails) |
Convincing deepfake audio/video, simulated calls with realistic voices |
|
Vulnerability Exploitation |
Manual scanning with limited tools |
AI discovers and exploits vulnerabilities in real time, faster than human teams |
|
Scale of Attacks |
Targeted attacks, relatively limited |
Massive, global attacks impacting thousands of organizations simultaneously |
From what has been explained above, it is clear that attacks initiated with AI have distinctive characteristics, and here are the 5 most prominent ones:
Characteristics of AI-Powered Cyberattacks
-
Attack Automation – AI enables cyberattacks to run automatically, reducing the need for human intervention.
-
Efficient Data Gathering – AI accelerates reconnaissance, finding targets and vulnerabilities faster and more accurately.
-
Customization – AI collects public data to craft hyper-personalized phishing and social engineering attacks.
-
Reinforcement Learning – AI adapts in real-time, improving attack techniques and evading detection.
-
Employee Targeting – AI identifies high-value individuals within organizations to maximize attack impact.
The Hidden AI Vulnerabilities Businesses Overlook in 2025
The year 2025 has been a year of surprises for us, with dozens of incidents where companies have suffered due to losing sight of the hidden risks that come with using AI at the enterprise level.
One of the recent cases that made a splash globally occurred in January-February 2025, when the artificial intelligence platform DeepSeek, a Chinese alternative to ChatGPT, faced a series of serious and complex security incidents. Let's recall the most notable incident - a massive data breach, in which over 1 million sensitive records, including conversation history, API keys, backend metadata, and access tokens, were all exposed due to a misconfigured (unauthenticated) ClickHouse database.
Also during the same period, DeepSeek was the victim of massive DDoS attacks that blocked new user registrations in order to defend its infrastructure. The platform has also been the target of supply chain attacks: fake packages on the Python Package Index (PyPI), designed to steal data from developers.
The DeepSeek 2025 case illustrates how fundamental technical vulnerabilities, incomplete configurations, weak protections, and a lack of security checks can lead to serious complications: massive data leaks, coordinated cyberattacks, and government bans. In deciphering this case, companies can take away a constructive lesson: AI infrastructure must be secured from the start, rigorously tested, and continuously monitored to avoid potentially devastating consequences.
Following these events, several countries (Italy, South Korea, the USA, Taiwan, the Netherlands, Australia, the Czech Republic, etc.) have imposed restrictions or banned the use of DeepSeek in the government environment, for security reasons.
Another example is the case from Arup 2024 that shows the real impact of deepfakes on critical financial decisions. In January 2024, an Arup employee in Hong Kong was targeted in a video conference that he believed was attended by the CFO and other senior colleagues. In reality, all the participants were fake people, with fake voices and faces that mimicked the appearance and speech of real people extremely well.
An article from the World Economic Forum notes:
"This wasn't a traditional cyberattack... People were deceived into believing they were carrying out genuine transactions."
As a result, 15 financial transfers, totaling HK$200 million (approximately US$25-26 million), were illegally requested to bank accounts controlled by the fraudsters. The incident was subsequently reported to Hong Kong police, and Arup later confirmed the loss of funds, but stated that its operations and internal systems were not compromised.
The Arop 2025 example was a surprising and unprecedented case, from which companies must understand that traditional digital security used so far is not enough. They must also put into operation advanced methods of identity verification, including real-time authentication and liveness detection technology, in order to effectively detect deepfakes and avoid the associated risks.
Therefore, you will find a structured list of the main artificial intelligence-powered risks and vulnerabilities that an organization or business could face in 2025.
AI-Powered Data Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
-
Shadow AI / Unauthorized AI Usage - Employees use AI models without IT approval, which can expose sensitive data and lead to privacy and compliance violations.
-
Data Poisoning & Adversarial AI/ML - Attackers introduce false data or manipulate inputs to compromise the integrity and accuracy of critical data sets.
-
Model Hijacking - AI models become targets of attack; once compromised, they can reveal stored sensitive data or generate erroneous responses that affect business decisions.
-
AI-Driven Social Engineering & Phishing - AI-driven personalized attacks target employees to gain access to confidential company credentials and data.
-
Deepfakes & Synthetic Identity Fraud - The use of fake identities or manipulated content to trick employees into gaining access to internal data or resources.
-
Malicious GPTs & AI-Generated Attack Tools - AI models are modified to generate fraudulent emails or malicious code, with the aim of extracting or compromising data.
-
AI-Enabled Ransomware - Uses AI to identify the most valuable data, quickly encrypt it, and more aggressively negotiate ransom.
-
Target Reconnaissance & Data Scraping - AI automates the massive collection of exposed data from public sources or internal networks for further attacks.
-
Fuzzing AI / Automated Vulnerability Testing - AI scans applications for bugs that can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to data.
Stay ahead of AI-driven risks!
Connect with top Cybersecurity, IT Security & Crime Prevention, and AI Security Management companies on TechBehemoths to find the right partner for your business.
Knowing the main types of AI-powered attacks defines for companies the vulnerabilities and risks they will theoretically have to deal with if they do not react quickly and consistently to current conditions, in which failure to adapt to new security requirements against AI attacks leads to serious consequences, both financially and reputationally, for the company.
What Businesses Need to Know: AI & Cybersecurity Regulations 2025
According to a study by IBM and Ponemon Institute, companies are adopting AI very quickly (“do-it-now”), but are not keeping up with the necessary security and governance rules. Thus, AI systems that are not well controlled and regulated are at greater risk of being attacked, and when they happen, organizations find themselves with high unforeseen costs.
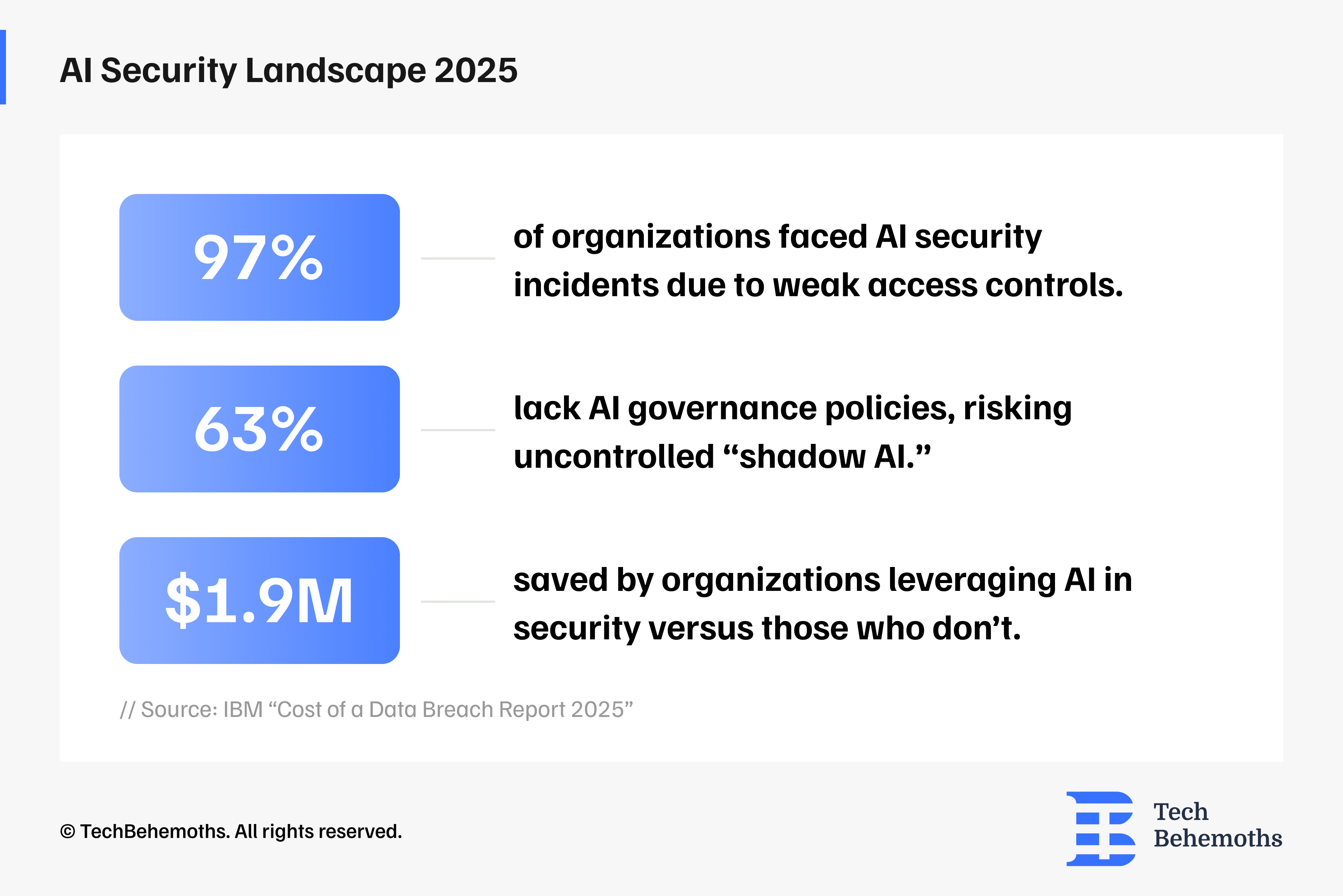
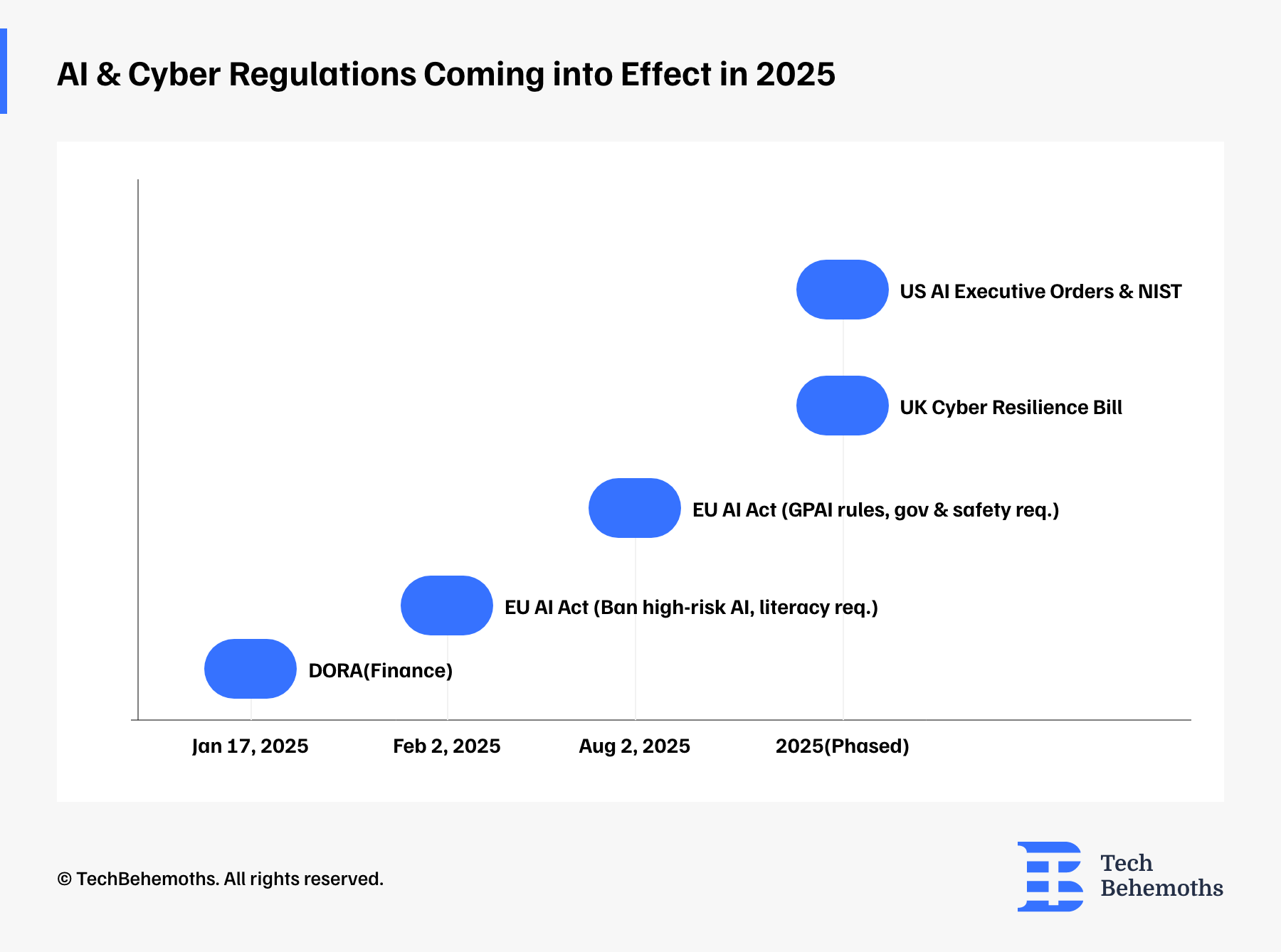
Let's now walk through the new regulations imposed on companies that significantly change how businesses will work with AI and data security in 2025 and beyond.
EU AI Act
EU AI Act is the world’s first comprehensive legal framework for AI, setting out a risk-based approach (from ignorable to unacceptable).
Entry into force: It entered into force on 1 August 2024, but the actual implementation is being phased in over 6–36 months.
2025 – First active obligations:
-
From 2 February 2025, bans on AI systems with unacceptable risk and AI literacy requirements start.
-
From 2 August 2025, key provisions on governance, privacy, and sanctions for the General Purpose AI (GPAI) model enter into force.
DORA — Digital Operational Resilience Act (Finance)
DORA is an EU regulation that requires financial institutions to secure their digital infrastructure: ICT risk, testing, incident reporting, operational resilience and third-party risks.
When it comes into force: It became mandatory from January 17, 2025.
UK Cyber Resilience / Security Bill
Extends the application of NIS regulations, increases requirements for incident reporting and increases the resilience of critical infrastructures.
USA — Executive Orders & NIST Frameworks
The U.S. administration issues executive orders that require government and industry to create safe, secure-by-design, explainable, and monitorable AI.
NIST has been tasked with developing guidelines for software security, communications, and digital identity in accordance with these executive orders.
|
Region |
Key Regulation |
Scope |
What Companies Must Do |
|---|---|---|---|
|
EU |
EU AI Act (2025) |
All industries, AI systems |
Classify AI by risk, ensure transparency, monitoring, explainability, and audits. |
|
DORA (Jan 2025) |
Financial sector |
Conduct resilience tests, implement incident response & continuity plans, report cyber incidents. |
|
|
UK |
Cyber Resilience Bill (expected 2025) |
Critical industries & services |
Mandatory cyber resilience, recovery plans, board accountability for cybersecurity. |
|
US |
AI Executive Order (2023, in force 2025) |
Federal agencies & private sector AI use |
Secure-by-design AI, risk assessments, transparency, consumer data protection. |
|
NIST AI RMF (2023–ongoing) |
AI risk management across industries |
Framework for accountability, monitoring, and safe AI deployment. |
Why is cybersecurity currently important for your business?
Companies can no longer sit idly by, and GDPR alone is not enough. In 2025, AI compliance means demonstrating that your AI systems are:
-
Explainable (easy to audit)
-
Continuously monitored
-
Secure by design
It’s about trust, accountability, and resilience - not just about avoiding fines.
Strategic AI Security Practices for 2025 and Beyond
Now more than ever, companies need to focus on how to solve the problem of data security and protect themselves from the risks of attacks generated by AI in the most cautious and long-term way possible.
Let's review the best practices for 2025 that every business must implement to strategically secure its data and information.
Six Pillars with Practical Steps for Business Resilience
-
Data encryption and privacy
Robust encryption and privacy-oriented design are the two essential elements with which you can start your company's data protection "reform". They must ensure that sensitive information is secured both at rest and in transit. The main steps to follow would be:
-
Using end-to-end encryption (at rest and in transit).
-
Implementing post-quantum cryptography for critical data.
-
Integrating privacy by design into all applications.
-
Access management and identity security
Access control is essential to prevent data security breaches and more, and applying the principle of least privilege and multi-factor authentication reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Here are some things to do:
-
Applying the principle of "least privilege" (access only to the strictest needs).
-
Implement multifactor authentication (MFA) and zero-trust frameworks.
-
Regularly audit access to sensitive data.
-
Secure AI training data
A basic criterion to consider when training AI is that the input data is clean and verifiable. Dataset integrity prevents data poisoning attacks and maintains algorithm performance, so what you will need to do is:
-
Verify and clean data sources to prevent data poisoning.
-
Maintain logs and traceability for all data sets.
-
Use data masking or synthetic data where possible.
-
Continuous monitoring and incident response
Constant monitoring allows for rapid identification of incidents, so there must be clear guidelines and automated alerts that can deliver an instant and controlled response. The minimum you could do in this direction is:
-
Implementing AI-based monitoring for data access and transfer.
-
Configuring automatic alerts for abnormal behavior.
-
Developing clear guidelines for rapid incident response.
-
Data lifecycle management
Comprehensive data management ensures long-term compliance and security. Therefore, automating secure deletion and documenting data flows are already mandatory practices. It would be beneficial to:
-
Classify data according to sensitivity and regulations.
-
Automate secure data deletion processes.
-
Document data flows and update them periodically.
-
Compliance and regulatory alignment
Compliance with regulations provides the company protection and builds a reputation of trust. Internal auditing and transparency in the use of AI ensure compliance with current and future legislation. Your actions in this regard would be the following:
-
Comply with EU AI Law, DORA, NIST, and GDPR.
-
Document how AI uses data and ensure transparency.
-
Implement internal audit and reporting processes.
Looking Ahead – The 2025–2030 Data Security Horizon
A scenario of the data security horizon from 2025-2030 is offered by the report entitled “Cybersecurity Futures 2030: New Foundations”, developed in collaboration between UC Berkeley’s Center for Long-Term Cybersecurity (CLTC), CNA’s Institute for Public Research, and the World Economic Forum’s Centre for Cybersecurity. It was signed, among others, by Akshay Joshi, Head of Industry and Partnerships at the World Economic Forum, who states:
“Leaders will need to strategically and tactically use regulation to guard against the downsides of AI products as they rise in prominence and take meaningful measures to combat [mis-, dis-, and mal-information] before it further degrades trust and unity.”
It is worth noting that the report is not only about IT security technology, but about the broader ecosystem of data and information security in the era of AI and disinformation. Specifically:
-
It shows how the increase in the use of AI and digital platforms intensifies the risks of data leaks, manipulation, and attacks.
-
It directly links data protection to trust – if data is compromised or manipulated (through mis-, dis- or mal-information), public trust and organizational stability decrease.
-
It emphasizes that future regulations will need to protect not only IT infrastructure, but also the integrity of the data and information that society consumes.
-
It provides leaders with a framework to combine classic cybersecurity (firewalls, encryption, incident response) with measures against data and information abuse.
During 2025-2030, the following solutions and focuses are expected to be implemented, such as unified cybersecurity platforms for data transparency, AI accountability and operational resilience to support business growth, the creation of secure technological environments at the enterprise level: dedicated browsers and other technologies to reduce phishing and prevent data breaches.
-
Inter-industry and public-private partnerships are also being pursued to address systemic challenges, including data privacy and combating disinformation.
-
Regarding adaptive regulations, as we discussed in the previous chapter, in 2025, a focus on AI, data protection, legal access to information and digital sovereignty begins at a global level.
-
Investments in the workforce and security by design also constitute a critical point, characterised by developing skills and integrating security from the design phase of systems.
Thus, while many traditional challenges will persist, the focus will shift to proactive solutions for data privacy, developing cybersecurity talent, combating disinformation, and increasing cyber resilience.

Conclusion
What businesses should take away from these deciphered things is that data is the most valuable and at the same time the most fragile resource in their organization, which is why the coming years will need maximum protection and vigilance more than ever.
Let's recognize that AI brings both the greatest risk and the greatest opportunity for the current business landscape, presenting duality in properties. It is able to act both as the first autonomous attacker, but also as the first defender of digital infrastructures, deserving both fear and admiration for those who deal with it.
It is important to detect risks and vulnerabilities in time and come up with appropriate solutions to them, to protect your business from attacks (AI-powered) on your data and sensitive information with the best practices and strategies.
Therefore, starting with 2025 and the next 5 years at least, data security will no longer be perceived as just a current cost, but will become an essential competitive differentiator for businesses, and the survival and credibility of a company will depend on how it treats data security in the AI era.
Related Questions & Answers
How are AI-powered attacks transforming cybersecurity threats in 2025?
What are the most common AI-driven cyberattack techniques in 2025?
How much did cyberattacks cost the German economy in 2025?
How many organizations lack maturity to counter AI-enabled threats?
What percentage of organizations lack foundational data and AI security practices?
What percentage of leaders report an increase in AI-powered attacks?